If an ESXi host member of the vSAN cluster fails for any reason, you should replace the failed host as soon as possible to avoid data loss.
It may happen a host fails or the ESXi installation gets corrupted with the result of disrupting provided services. If the vSAN cluster is well designed, data stored in the vSAN storage are still available even if a host fails, but data integrity and availability cannot be guaranteed if also a second host fails.
Failed hardware must be replaced and the ESXi reinstalled as soon as possible leaving the disks used in the vSAN storage untouched (if the disk is not the failed component of course) to preserve the logical structure.
Replace the failed host
Once the failed hardware has been replaced or the ESXi reinstalled, power on the host. Select the vSAN cluster and go to Monitor > vSAN area to check the health status of the vSAN. The State of the replaced host should be reported as Abnormal if a fresh installation was required to restore the host functionality. Pretty clear that something wrong is occourring in the vSAN cluster.
Check vSAN cluster status
To figure out what's going on with the replaced host, you have to operate at the host level checking the cluster status using esxcli commands. Enable the SSH service in the replaced ESXi host and login with the root credentials.
From the console run the following command to get information of the vSAN cluster:
# esxcli vsan cluster get
As expected, the new host is not member of any vSAN cluster because the fresh installation procedure deleted all configuration settings. If an up-to-date host's configuration backup is available, you can save lot of time in the restore configuration process.
Join the replaced host to vSAN cluster
To join the host to the vSAN cluster, you need to know the correct UUID in use. SSH a working ESXi member of the vSAN cluster to retrieve the UUID and run the following esxcli command:
# esxcli vsan cluster get
Once the UUID number has been identified, write down the number (or simply copy it) and go back to the console of the replaced host. To join the new host to the vSAN cluster, run the command from the replaced host's console:
# esxcli vsan cluster join -u <UUID>
where the UUID is the number you previously noted.
When the process has completed, run the following command once again to get the vSAN cluster info:
# esxcli vsan cluster get
The new ESXi host is now member of the vSAN cluster.
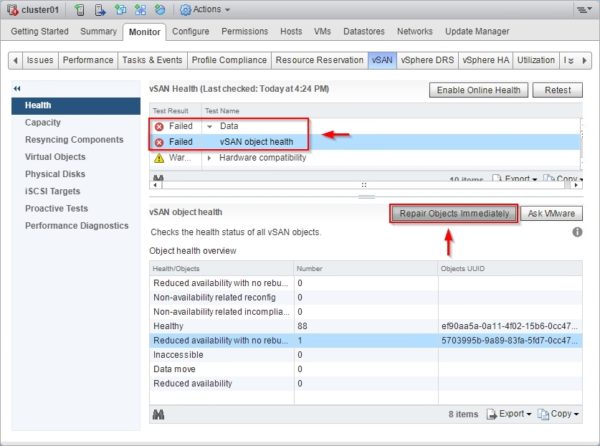
From the vSphere Web Client, select the vSAN cluster and go to Monitor > vSAN section. Click Retest button to check the health status.
Some errors are still reported related to data availability. To fix the problem, click Repair Objects Immediately button.
The Health status looks more much better now and the vSAN datastore is operating properly.
In the Datastores area, the vSAN Status is reported as Normal.
Make sure to have a robust design for your vSAN cluster and a good backup strategy in place to avoid data loss in the situation the vSAN cannot be restored.