A working mail server can be configured using Postfix (MTA) with the addition of some components like Dovecot (IMAP) and Roundcube (webmail).
Combining these applications we obtain an email system with SMTP, IMAP, POP3 protocols that can be used in a corporate environment where the budget is pretty limited. This solution is based on Open Source software where no licenses need to be purchased for its use.
Prerequisites
- CentOS 6: minimal installation
- Postfix: SMTP
- Dovecot: IMAP, POP3
- Roundcube: web-based IMAP client
- Postfix admin: to easily manage Postfix
To work properly, system needs to have selinux disabled.
# vi /etc/selinux/config
Install Postfix
From the console, install Postfix with yum command.
# yum install postfix
Edit configuration file /etc/postfix/main.cf and set the parameters as follow:
myhostname = hostname.domain.com mydomain = domain.com myorigin = $mydomain inet_interfaces = all mydestination = $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost, $mydomain mynetworks = 192.168.1.0/24, 127.0.0.0/8 home_mailbox = Maildir/
# vi /etc/postfix/main.cf
myhostname = hostname.domain.com mydomain = domain.com myorigin = $mydomain
inet_interfaces = all
mydestination = $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost, $mydomain
mynetworks = 192.168.1.0/24, 127.0.0.0/8
home_mailbox = Maildir/
Once all the parameters have been set, set application to start during system boot and start the service.
# chkconfig postfix on
# service postfix start
Testing Postfix
To check if everything works as expected, type from console the following commands to send an email:
# telnet localhost smtp
Trying ::1... Connected to localhost. Escape character is '^]'. 220 server.domain.com ESMTP Postfix ehlo localhost 250-server.domain.com 250-PIPELINING 250-SIZE 10240000 250-VRFY 250-ETRN 250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES 250-8BITMIME 250 DSN mail from: username@domain.com 250 2.1.0 Ok rcpt to: username@domain.com 250 2.1.5 Ok data 354 End data with <CR><LF>.<CR><LF> test . 250 2.0.0 Ok: queued as 2C55A94 quit 221 2.0.0 Bye Connection closed by foreign host.
To check if the email has been received, have a look at the /home/username/Maildir/new directory.
# cd /home/username/Maildir/new/
# ll
# cat xxxxx.xxxxx.server.domain.com
The email was received by the system then the mail server is working properly.
Install Dovecot
While Postfix acts as Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) only, in order to retrieve emails using modern tools we need to enable IMAP/POP3 protocols. Dovecot is an application that acts as a secure IMAP and POP3 server.
Use the yum command to install Dovecot.
# yum install dovecot
Edit the configuration file /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf to enable the needed protocols.
# vi /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf
protocols = imap pop3 lmtp
Then we need to specify the mail location by editing the file /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf.
# vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf
mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir
Edit the file /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf and set the following parameters:
# vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf
disable_plaintext_auth = no
auth_mechanisms = plain login
Last file to edit /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-master.conf.
# vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-master.conf
unix_listener auth-userdb {
#mode = 0600
user = postfix
group = postfix
}
Set Dovecot to start at system boot and start the service.
# chkconfig dovecot on
# service dovecot start
Testing Dovecot
To check if Dovecot is working, we test the program through the POP3 protocol.
# telnet localhost pop3
Trying ::1... Connected to localhost. Escape character is '^]'. +OK Dovecot ready. user admin +OK pass password +OK Logged in. list +OK 1 messages: 1 477 . retr 1 +OK 477 octets Return-Path: <username@domain.com> X-Original-To: username@domain.com Delivered-To: username@domain.com Received: from localhost (localhost [IPv6:::1]) by server.domain.com (Postfix) with ESMTP id 2C55A94 for username@domain.com; Wed, 12 Jun 2013 12:22:00 +0200 (CEST) Message-Id: <20130207113547.117113FF18@server.domain.com> Date: Wed, 12 Jun 2013 12:22:00 +0200 (CEST) From: username@domain.com To: undisclosed-recipients:; test postfix . quit +OK Logging out. Connection closed by foreign host.
Install Roundcube
Roundcube is a browser-based IMAP client with an application-like user interface.
To configure the application, firstly we need to install MySQL server and Apache in the system.
# yum install mysql-server mysql-devel httpd
Enable both MySQL and Apache to start at system boot and enable services.
# chkconfig mysqld on
# service mysqld start
# chkconfig httpd on
# service httpd start
Install EPEL repository
To install Roundcube with yum command, we need to install the EPEL repository in the system.
# wget http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
# rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
Once EPEL repo has been installed, use yum to install Roundcube.
# yum install roundcubemail
Configure MySQL
To define the database used by the application, we need to access MySQL configuration.
# mysql -u root -p
mysql> create database roundcube; mysql> create user roundcube; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON roundcube.* TO roundcube@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; mysql> flush privileges; mysql> use roundcube; mysql> source /usr/share/doc/roundcubemail-0.8.6/SQL/mysql.initial.sql mysql> quit
Edit configuration file /etc/roundcubemail/db.inc.php to set the parameters to access the database.
# vi /etc/roundcubemail/db.inc.php
$rcmail_config['db_dsnw'] = 'mysql://roundcube:password@localhost/roundcube';
Edit the file /etc/roundcubemail/main.inc.php to set the hostname chosen to perform the login.
# vi /etc/roundcubemail/main.inc.php
$rcmail_config['default_host'] = 'localhost';
To make the system accessible outside the server, edit the file /etc/httpd/conf.d/roundcubemail.conf and set the correct parameter.
# vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/roundcubemail.conf
Allow from all
Edit the /etc/php.ini file and set the time zone.
Because the log could report errors related to encryption, set the correct encryption parameter.
# vi /etc/php.d/mcrypt.ini
extension=mcrypt.so
Restart Apache.
# service httpd restart
Testing Roundcube
Access Roundcube typing from your browser the address:
http://IP_address/roundcubemail
Enter your credential then click Login.
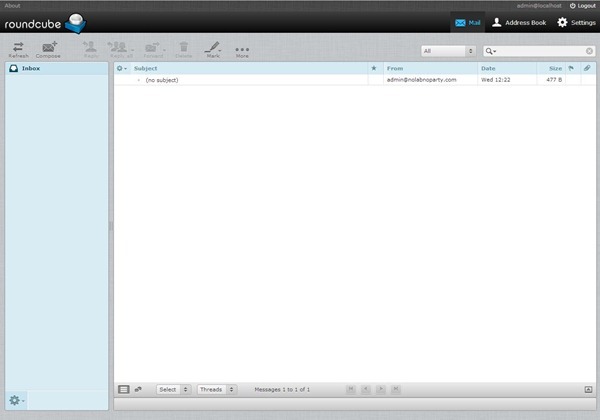
The main screen appears showing the email received when Postfix was previously tested.
Install Postfix Admin
To make Postfix administration easier, the Postfix admin is a web-based tool used to manage mailboxes, virtual domains and aliases.
If not already present in the system, install the PHP component needed by the application.
# yum install php-imap
Access MySQL and create the database used by Postfix Admin.
# mysql -u root -p
mysql> create database postfixadmin; mysql> grant all privileges on postfixadmin.* to postfixadmin@'localhost' identified by 'password'; mysql> flush privileges; mysql> quit
Using the wget command, download the latest release of the application.
# wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/postfixadmin/postfixadmin/postfixadmin-2.3.6/postfixadmin-2.3.6.tar.gz
Extract the content and move the directory to /var/www/html folder.
# tar -vxzf postfixadmin-2.3.6.tar.gz
# mv postfixadmin-2.3.6 /var/www/html/postfixadmin
Edit the configuration file /var/www/html/postfixadmin/config.inc.php to enable the application and set the password.
# vi /var/www/html/postfixadmin/config.inc.php
$CONF['configured'] = true; $CONF['setup_password'] = 'password';
Set the correct parameters to access the database previously created.
$CONF['database_type'] = 'mysqli'; $CONF['database_host'] = 'localhost'; $CONF['database_user'] = 'postfixadmin'; $CONF['database_password'] = 'password'; $CONF['database_name'] = 'postfixadmin';
Add the following line to allow the creation of the administration password.
$CONF['setup_password'] = '8abd38580e77ebf7010eb60b95eb4fad:0bd829114d9efc4bc35c7e42cf7d3507dad8b837';
Restart Apache.
# service httpd restart
To execute the Postfix Admin Setup Checker, type in your browser the address:
http://IP_address/postfixadmin/setup.php
Change the setup password.
Create the Superadmin account by filling the fields at the bottom of the screen. Click Add Admin.
The Superadmin account is then created.
To access the Administration interface, type in your browser the address:
http://IP_address/postfixadmin
The Postfix Admin main screen.
Sending emails through a relay
If the corporate network has an antispam system to check inbound and outbound emails, Postfix needs to be configured in order to relay the emails to the antispam.
To allow the correct emails flow, set the relayhost field with the address of the antispam system.
# vi /etc/postfix/main.cf
relayhost= lx-antispam02.nolabnoparty.local
The mail server is now up and running with the basic functions to properly manage email messages.


















































Thanks a lot!!! my new mailserver is running!
très bon documentation , tank's ^^
If I understand postfix.admin function correctly, it can be used to create new email account for users am I right?
Thanks in advance.
Hi;
I have configured the server with the above configuration. But I am not able to change password after enabling the password change plugin. says "Could not save New Password"
hello,
Thanks for this doc. I have set up a server using the steps you laid out and everything is working except all the incoming mail is ending up in the root mail box and not in the user mailboxes. Do you have any idea why this is happening?
I have configured the mailserver with above configuration but I am getting error on roundcube login page, that saya "connection to storage server failed", I am using system user for login
Thanks for the nice post. But when I add a user using postfix admin its not recognised by roundcube even on mail server. But i can log in round cube and mail server with my system account. please help
Yeahhh... me too
Will be glad if paolo can help our both case 🙂
i follow all your tutorial and always end whit this error:
IMAP Error in /usr/share/roundcubemail/program/lib/Roundcube/rcube_imap.php (184): Login failed for rhega@kreasimediaonline.com from 182.xxx.xxx.xxx. AUTHENTICATE PLAIN: Authentication failed.
will be checking this post everyday to know any solution from paolo or others 😀
hi , i had the same problem .
you should restart your browser and then enter /ip-address/postfixadmin to login .
Hi,
Really very usefull website, I have configured the same, it is working fine. Thanks
Please post the same to vacation email setting
to help full for all.
Thanks for advance
Thanks
Ramesh
hugelol/fail as you wish...
you say people should disable selinux. That's wrong, if selinux is activated on their machine, they should simply configure it, not disable it.
then autorize plaintext auth? SERIOUSLY? why? o_O
I'll stop my reading here ^^
hi sir. can you explain about this code " ' " ?
It's a HTML escapes code: ' = ' (single quote).
The instruction should be: Escape character is '^]'.
Wonderful work. All the steps explained well and able to achieve what I want.
Thanks and keep this wonderful work.
Thank you.
I appreciate your interest in my work...
I follow your approach to complete the installation. Appears a problem. Unable to log into roundcube.
My first contact with roundcube. Ask what the first login user name and password?
Log information content:
[01-Aug-2014 15:36:00 +0800]: IMAP Error: Login failed for root from 192.168.16.111 AUTHENTICATE PLAIN:... * BYE Internal error occurred Refer to server log for more information in / usr / share / round
cubemail / program / lib / Roundcube / rcube_imap.php on line 184 (POST / roundcubemail /? _ task = login & _action = login)
I need your help. thank you very much...
nice tutorial but I have configure mail server successfully with postifixadmin, but I am getting 1 error when I have create mail id via postfix admin then login on roundcube I am getting error invalid user or password.
but when I have create user on system via command line (useradd username), then login on roundcube successfully please give me solution
I have a same problem
After I installed roundcube, it says:
DATABASE ERROR: CONNECTION FAILED!
Unable to connect to the database!
Please contact your server-administrator.
I restart mysql,http,postfix,roundcube but the message still there!
Please help me.
unable to login postfixadmin users to roundcube mail, dear polo fix it
great tutorial but i dont know how to add new user (i can create more user at the machine and it will work buts thats not mi idea) i want to log at roundcube only whit the username and dont the entire dir ex: rvenegas@mydomain.com