Moving an existing RDM from one virtual machine to another some steps are required to avoid data loss and to keep the disk configuration.
The RDM allows a virtual machine to directly access and use the storage device and before proceeding with the move, the virtual machine where the RDM is currently attached must be shut down.
From vSphere Web Client (vSphere 5.5 has been used in the example), right click the VM to process and select Shutdown Guest OS option.

Click Yes to confirm the shut down.

Remove the RDM
From vSphere Web Client, select the VM and click Edit Settings in the VM Hardware area.
Keep in mind this procedure destroys the mapping file, not the LUN content.

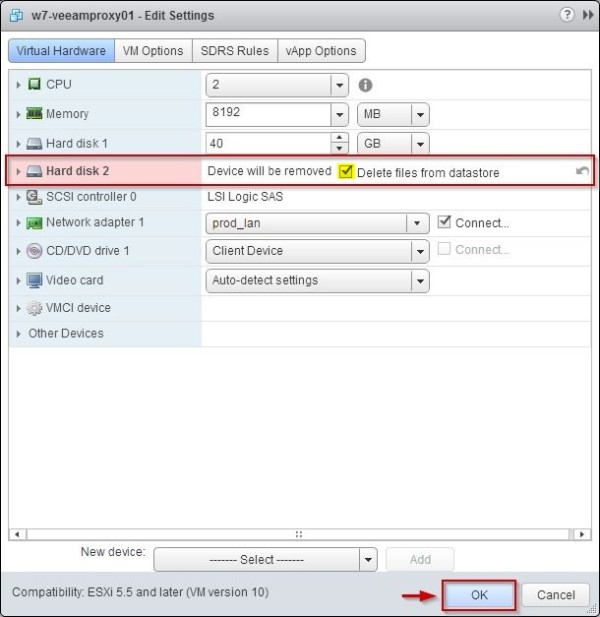
Identify the RDM hard disk to remove.

Click on the 'x' sign to remove the disk.

Enable Delete files from datastore option then click OK.
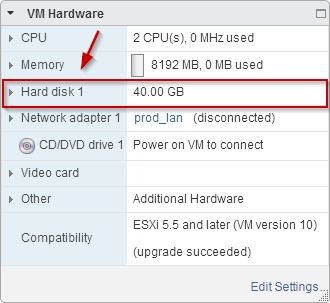
Hard disk 2 has been removed from the VM. LUN and its contenut are not altered during this step.
Attach the RDM to the new VM
In the new virtual machine, click Edit Settings under the VM Hardware area.
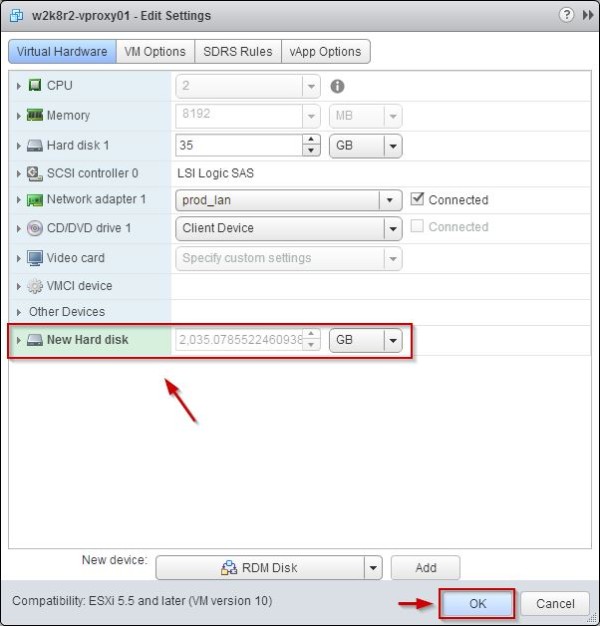
In the New device field, click the right arrow to open the drop-down menu and select RDM Disk option.
Click Add button.
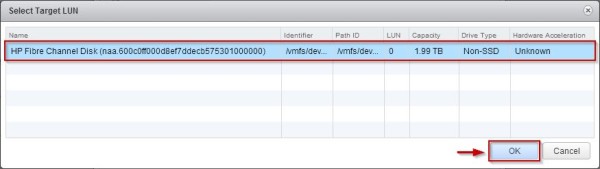
From the list of SAN disks or LUNs, select the LUN to access directly and click OK.
Click on the just attached New Hard disk and select the appropriate Compatibility Mode (i.e. Physical).
Click OK to save the configuration.
The new RDM disk (Hard disk 2) is now attached to the VM.
Access the processed virtual machine (a Windows VM in the example) and open the Disk Management tool. Right click the new attached disk and select Online option.
The partition previously configured in the old VM is retained and is now available to the new VM.
To check if the RDM move procedure have been completed successfully, try accessing files and folders using Windows Explorer.
As best practice, before moving disks and LUNs be sure to have a full working backup.