After the vulnerabilities Spectre and Meltdown, a recently identified speculative execution side-channel method called L1 Terminal Fault (L1TF) has been shared from Intel.
Similar to Spectre and Meltdown issues, L1TF vulnerability affects only Intel Core and Xeon processors where a malicious code running in these CPUs could read data it is not entitled to from another process.
VMware already released some patches to fix this problem as reported in the VMware Security Advisories VMSA-2018-0020. Since the process to identify affected hosts may take some time, solutions like Runecast Analyzer can help to identify critical hosts in matter of seconds.
VMware L1TF patches
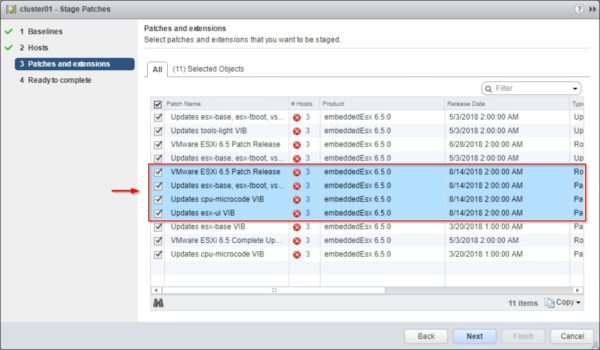
On August, 14th 2018 VMware released some patches for vCenter Server and ESXi to mitigate L1TF vulnerability.
vCenter Server
VMware released vCenter Server patches for the following releases:
- vCenter Server 6.7 - VC 6.7.0d build 9451876
- vCenter Server 6.5 - VC 6.5 Update 2c - build 9451637
- vCenter Server 6.0 - VC 6.0 Update 3h - build 9451619
- vCenter Server 5.5 - VC 5.5 Update 3j - build 9313450
To patch the vCenter Server proceed as you normally do when new updates are released.
If the vCSA is used in your infrastructure, patches can be applied using the VAMI.
If you run the vCenter Server Windows-based version, Microsoft patches must be applied also to the guest OS because the L1TF creates vulnerabilities at the OS level.
ESXi
Once the vCenter Server has been patched, you need to patch the ESXi hosts installed in your infrastructure.
VMware released ESXi patches for the following releases:
- ESXi 6.7 - ESXi670-201808401-BG
- ESXi 6.5 - ESXi650-201808401-BG
- ESXi 6.0 - ESXi600-201808401-BG
- ESXi 5.5 - ESXi550-201808401-BG
Patches for ESXi already include the code to patch the affected CPUs without installing BIOS or firmware updates released from the hardware vendor.
ESXi hosts can be easily updated using VUM.
Mitigate the L1TF issue
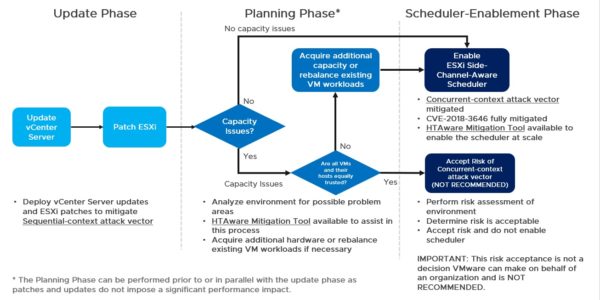
In the KB55806, VMware reports the procedure to mitigate the CVE-2018-3646 vulnerability that includes a three phases process:
- Update Phase: apply vSphere updates and patches. vCenter Server must be patched first to avoid problems then the ESXi hosts.
- Planning Phase: assess the environment to understand if sufficient CPU capacity is available to avoid operational impacts enabling the ESXi Side-Channel-Aware Scheduler needed to mitigate the Concurrent-context attack vector.
- Scheduler-Enablement Phase: enable the ESXi Side-Channel-Aware Scheduler.
Enabling the ESXi Side-Channel-Aware Scheduler
After applying the above patches to ESXi hosts installed in your network, you need to enable the ESXi Side-Channel-Aware Scheduler to complete the fix process.
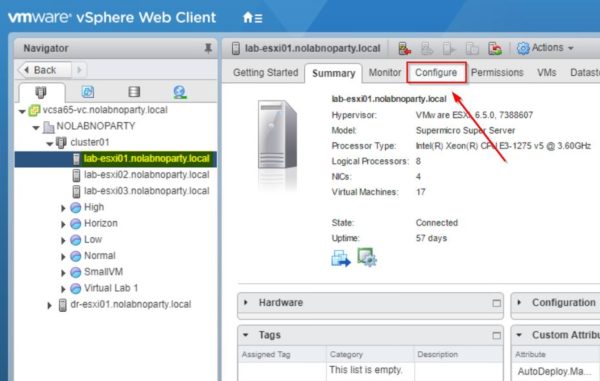
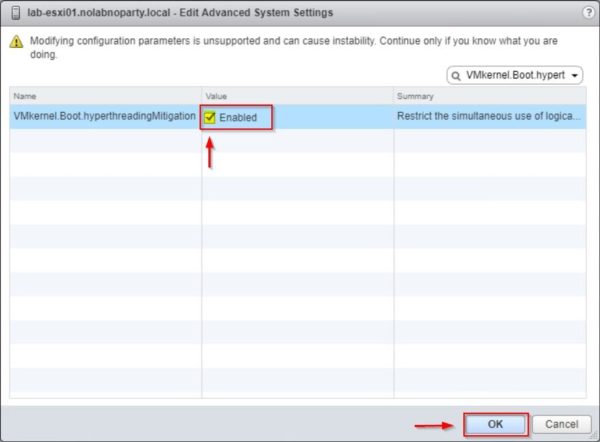
From the vSphere Web Client (you can also use the vSphere Client or the ESXi Embedded Host Client) select the ESXi host to process and click the Configure tab.
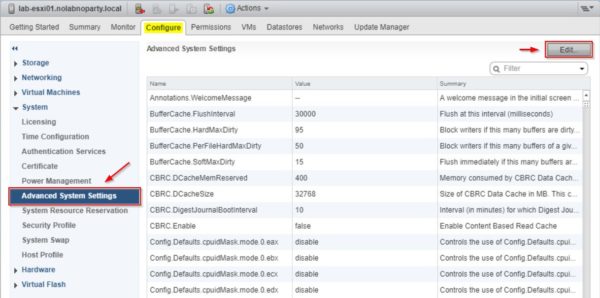
Select Advanced System Settings under System item and click the Edit button.
Search for VMkernel.Boot.hyperthreadingMitigation in the Filter box.
By default this parameter is disabled. Set the configuration option to Enabled and click OK to confirm.
Reboot the ESXi host to apply changes.
ESXi Side-Channel-Aware Scheduler impact
Enabling the ESXi Side-Channel-Aware Scheduler, you may experience some performance issues with a service degradation. Before enabling this parameter read carefully the KB55767.
Due to these limitations, the ESXi Side-Channel-Aware Scheduler is disabled by default and it's up to the administrators/organizations to enable this parameter. Leaving the scheduler disabled exposes the host to the risk posed by the Concurrent-context attack vector.